log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.SparkEnv=DEBUGSparkEnv — Spark Runtime Environment
Spark Runtime Environment (SparkEnv) is the runtime environment with Spark’s public services that interact with each other to build the entire Spark computing platform for a Spark application.
Spark Runtime Environment is represented by a SparkEnv object that holds all the required runtime services for a running Spark application with separate environments for the driver and executors.
| Property | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|
serializer |
Serializer |
|
closureSerializer |
Serializer |
|
serializerManager |
SerializerManager |
|
mapOutputTracker |
MapOutputTracker |
|
shuffleManager |
ShuffleManager |
|
broadcastManager |
BroadcastManager |
|
blockManager |
BlockManager |
|
securityManager |
SecurityManager |
|
metricsSystem |
MetricsSystem |
|
memoryManager |
MemoryManager |
|
outputCommitCoordinator |
OutputCommitCoordinator |
|
Tip
|
Enable Add the following line to Refer to Logging. |
SparkEnv Factory Object
SparkEnv holds the public services in a running Spark instance, using SparkEnv.createDriverEnv() for a driver and SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv() for an executor.
You can access the Spark environment using SparkEnv.get.
scala> import org.apache.spark._
import org.apache.spark._
scala> SparkEnv.get
res0: org.apache.spark.SparkEnv = org.apache.spark.SparkEnv@2220c5f7 Creating "Base" SparkEnv — create Method
create(
conf: SparkConf,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
port: Int,
isDriver: Boolean,
isLocal: Boolean,
numUsableCores: Int,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus = null,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnvcreate is a internal helper method to create a "base" SparkEnv regardless of the target environment — be it a driver or an executor.
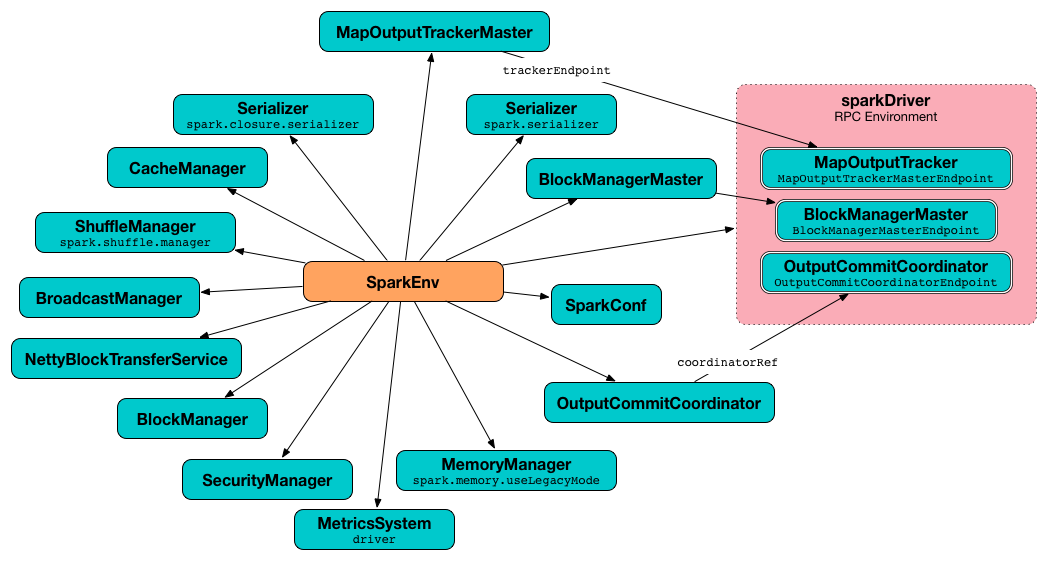
When executed, create creates a Serializer (based on spark.serializer setting). You should see the following DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG SparkEnv: Using serializer: [serializer]It creates another Serializer (based on spark.closure.serializer).
It creates a ShuffleManager based on spark.shuffle.manager setting.
It creates a MemoryManager based on spark.memory.useLegacyMode setting (with UnifiedMemoryManager being the default).
It creates a NettyBlockTransferService.
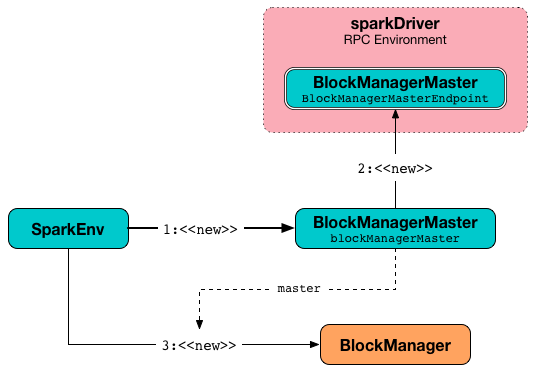
It creates a BlockManagerMaster object with the BlockManagerMaster RPC endpoint reference (by registering or looking it up by name and BlockManagerMasterEndpoint), the input SparkConf, and the input isDriver flag.
|
Note
|
create registers the BlockManagerMaster RPC endpoint for the driver and looks it up for executors.
|
It creates a BlockManager (using the above BlockManagerMaster object and other services).
It creates a BroadcastManager.
It creates a CacheManager.
It creates a MetricsSystem for a driver and a worker separately.
It initializes userFiles temporary directory used for downloading dependencies for a driver while this is the executor’s current working directory for an executor.
An OutputCommitCoordinator is created.
|
Note
|
create is called by createDriverEnv and createExecutorEnv.
|
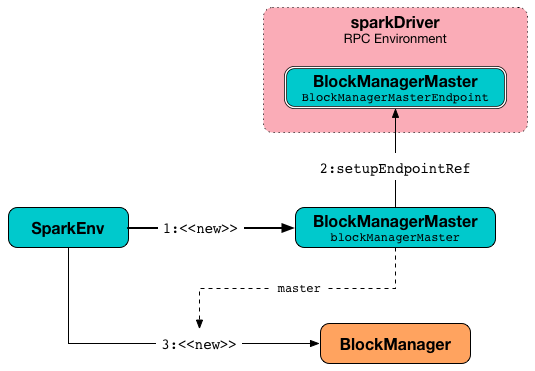
Registering or Looking up RPC Endpoint by Name — registerOrLookupEndpoint Method
registerOrLookupEndpoint(name: String, endpointCreator: => RpcEndpoint)registerOrLookupEndpoint registers or looks up a RPC endpoint by name.
If called from the driver, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO SparkEnv: Registering [name]And the RPC endpoint is registered in the RPC environment.
Otherwise, it obtains a RPC endpoint reference by name.
Creating SparkEnv for Driver — createDriverEnv Method
`createDriverEnv`(
conf: SparkConf,
isLocal: Boolean,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus,
numCores: Int,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnvcreateDriverEnv creates a SparkEnv execution environment for the driver.
The method accepts an instance of SparkConf, whether it runs in local mode or not, LiveListenerBus, the number of driver’s cores to use for execution in local mode or 0 otherwise, and a OutputCommitCoordinator (default: none).
createDriverEnv ensures that spark.driver.host and spark.driver.port settings are set in conf SparkConf.
It then passes the call straight on to the create helper method (with driver executor id, isDriver enabled, and the input parameters).
|
Note
|
createDriverEnv is exclusively used by SparkContext to create a SparkEnv (while a SparkContext is being created for the driver).
|
Creating SparkEnv for Executor — createExecutorEnv Method
createExecutorEnv(
conf: SparkConf,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
port: Int,
numCores: Int,
isLocal: Boolean): SparkEnvcreateExecutorEnv creates an executor’s (execution) environment that is the Spark execution environment for an executor.
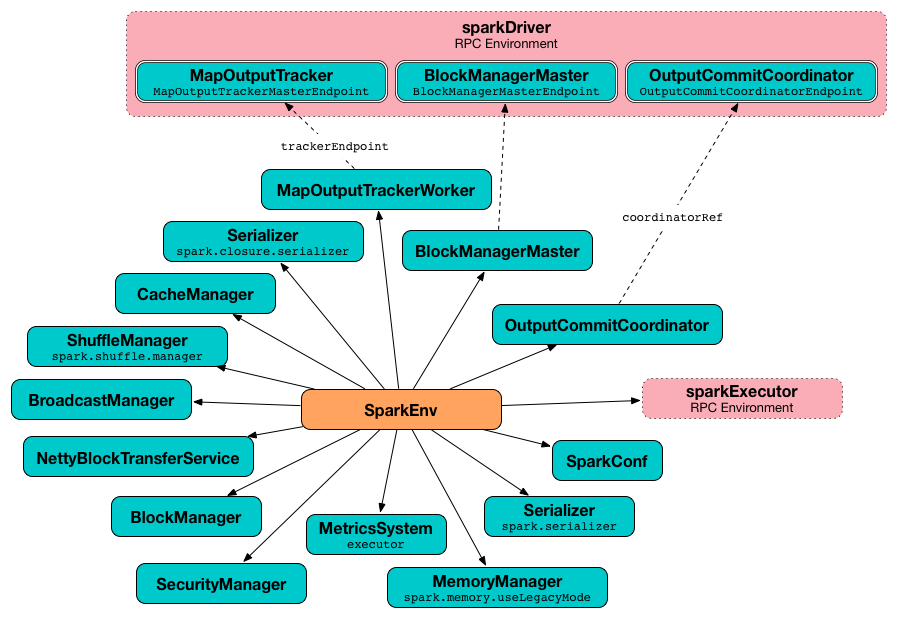
It uses SparkConf, the executor’s identifier, hostname, port, the number of cores, and whether or not it runs in local mode.
It creates an MapOutputTrackerWorker object and looks up MapOutputTracker RPC endpoint. See MapOutputTracker.
It creates a MetricsSystem for executor and starts it.
An OutputCommitCoordinator is created and OutputCommitCoordinator RPC endpoint looked up.
serializer
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
closureSerializer
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
Getting Current SparkEnv — get Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
stop Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
Settings
| Spark Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
The name of the machine where the driver runs on. It is set when |
||
|
The port the driver listens to. It is first set to |
|
|
The [TIP]
====
Enable DEBUG logging level for
|
|
|
The |
|
|
The flag to control the MemoryManager in use. When enabled ( |