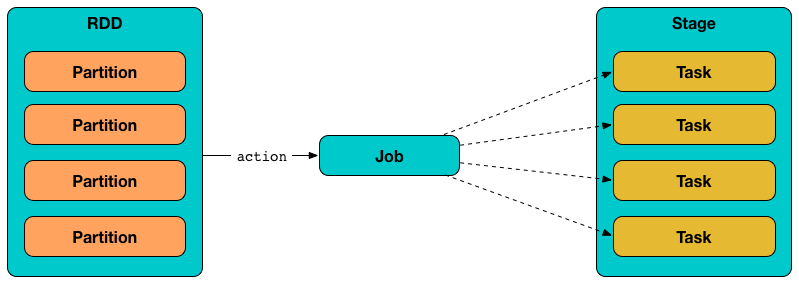
Tasks
In Spark, a task (aka command) is the smallest individual unit of execution that represents a partition in a dataset and that an executor can execute on a single machine.

In other (more technical) words, a task is a computation on a data partition in a stage in a job.
A task can only belong to one stage and operate on a single partition. All tasks in a stage must be completed before the stages that follow can start.
Tasks are spawned one by one for each stage and partition.
|
Caution
|
FIXME What are stageAttemptId and taskAttemptId?
|
A task in Spark is represented by the Task abstract class with two concrete implementations:
-
ShuffleMapTask that executes a task and divides the task’s output to multiple buckets (based on the task’s partitioner).
-
ResultTask that executes a task and sends the task’s output back to the driver application.
The very last stage in a job consists of multiple ResultTasks, while earlier stages are a set of ShuffleMapTasks.
Task Attributes
A Task instance is uniquely identified by the following task attributes:
-
stageId- there can be many stages in a job. Every stage has its own uniquestageIdthat the task belongs to. -
stageAttemptId- a stage can be re-attempted for execution in case of failure.stageAttemptIdrepresents the attempt id of a stage that the task belongs to. -
partitionId- a task is a unit of work on a partitioned distributed dataset. Every partition has its own uniquepartitionIdthat a task processes. -
metrics- an instance of TaskMetrics for the task. -
localProperties- local private properties of the task.
Running Task Thread — run Method
run(
taskAttemptId: Long,
attemptNumber: Int,
metricsSystem: MetricsSystem): Trun registers task attempt id to the executor’s BlockManager and creates a TaskContextImpl that in turn gets set as the thread local TaskContext.
If the task has been killed before the task runs it is killed (with interruptThread flag disabled).
The task runs.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Describe catch and finally blocks.
|
|
Note
|
When run is called from TaskRunner.run, the Task has just been deserialized from taskBytes that were sent over the wire to an executor. localProperties and TaskMemoryManager are already assigned.
|
Running Task — runTask Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
Task States
A task can be in one of the following states:
-
LAUNCHING -
RUNNINGwhen the task is being started. -
FINISHEDwhen the task finished with the serialized result. -
FAILEDwhen the task fails, e.g. whenFetchFailedException(see FetchFailedException),CommitDeniedExceptionor anyThrowableoccur -
KILLEDwhen an executor kills a task. -
LOST
States are the values of org.apache.spark.TaskState.
|
Note
|
Task status updates are sent from executors to the driver through ExecutorBackend. |
Task is finished when it is in one of FINISHED, FAILED, KILLED, LOST
LOST and FAILED states are considered failures.
|
Tip
|
Task states correspond to org.apache.mesos.Protos.TaskState. |
Collect Latest Values of Accumulators — collectAccumulatorUpdates Method
collectAccumulatorUpdates(taskFailed: Boolean = false): Seq[AccumulableInfo]collectAccumulatorUpdates collects the latest values of accumulators used in a task (and returns the values as a collection of AccumulableInfo).
|
Note
|
It is used in TaskRunner to send a task’s final results with the latest values of accumulators used. |
When taskFailed is true it filters out accumulators with countFailedValues disabled.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Why is the check context != null?
|
|
Note
|
It uses context.taskMetrics.accumulatorUpdates().
|
|
Caution
|
FIXME What is context.taskMetrics.accumulatorUpdates() doing?
|
Killing Task — kill Method
kill(interruptThread: Boolean)kill marks the task to be killed, i.e. it sets the internal _killed flag to true.
It calls TaskContextImpl.markInterrupted when context is set.
If interruptThread is enabled and the internal taskThread is available, kill interrupts it.
|
Caution
|
FIXME When could context and interruptThread not be set?
|
ShuffleMapTask
A ShuffleMapTask divides the elements of an RDD into multiple buckets (based on a partitioner specified in ShuffleDependency).
ResultTask
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
taskMemoryManager attribute
taskMemoryManager is the TaskMemoryManager that manages the memory allocated by the task.